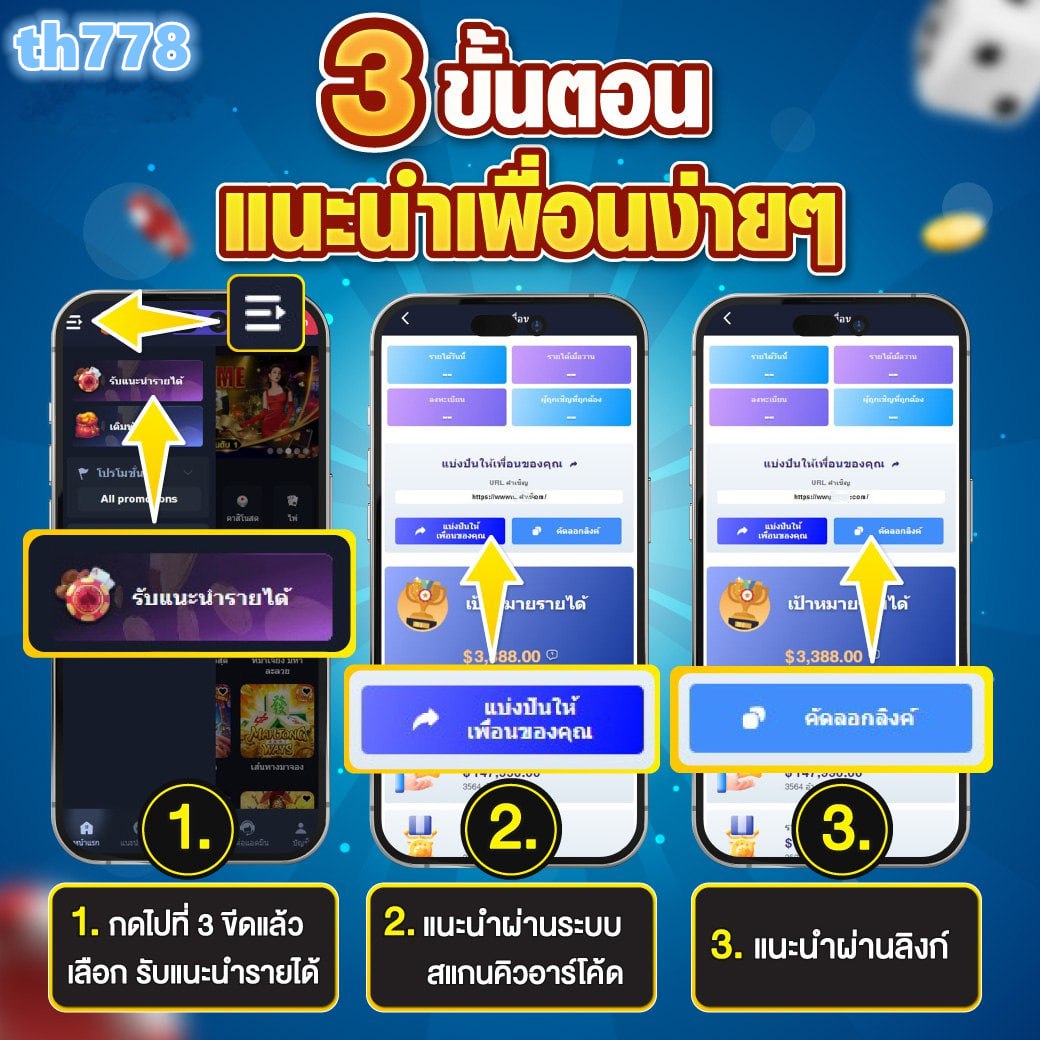
globalbet สล็อต
฿10.00
globalbet สล็อต lv244สล็อต GLOBALBET สล็อตเว็บดังอันดับ 1 ของโลก แตกง่าย แตกบ่อย ฝากถอนอัตโนมัติ ทดลองเล่นฟรีทุกค่าย ทุกเกมดัง บริการที่ยอดเยี่ยมและระบบที่ทันสมัย
sora168 สล็อต GlobalBet is the leading virtual sports and betting solutions provider, delivering innovative and reliable products to more than 100 operators worldwide
ของแทร่ 1688 สล็อต เกมพนันออนไลน์เว็บ globalbet คาสิโนออนไลน์ เว็บตรง เว็บใหญ่จ่ายจริง ฝาก-ถอนไม่มีขั้นต่ำ ด้วยระบบ Auto รวดเร็วใน 3 นาที
moowhan 888 สล็อต GLOBALBET เว็บพนันออนไลน์อันดับ 1 ที่รวบรวม คาสิโนออนไลน์อย่างครบถ้วน ทั้งคาสิโนสด เกมส์สล็อตออนไลน์ พร้อมทั้งตัวเกมส์ใหม่แบบ อี-สปอร์ต เพื่อมอบความหลากหลายให้ท่านได้ใช้บริการ
Add to wish list- SKU:627412331
- Category:Game
- Tags:globalbet สล็อต
Product description
globalbet สล็อตglobalbet สล็อต ✅ GLOBALBET สล็อตเว็บดัง ยอดนิยม อันดับ 1 ของโลก แตกบ่อย globalbet สล็อต,GLOBALBET สล็อตเว็บดังอันดับ 1 ของโลก แตกง่าย แตกบ่อย ฝากถอนอัตโนมัติ ทดลองเล่นฟรีทุกค่าย ทุกเกมดัง บริการที่ยอดเยี่ยมและระบบที่ทันสมัย &emspGlobalbet - 0 สล็อตออนไลน์ ✓ 12 คาสิโนออนไลน์ ✓ โบนัสแบบไม่ต้องมีเงินฝาก Globalbet ที่ดีที่สุด ✓ การหมุนฟรี Globalbet ที่ดีที่สุด