buddy88 สล็อต
฿10.00
buddy88 สล็อต เว็บสล็อต betflik buddy88 หากคุณกำลังมองหา เว็บสล็อต ที่น่าเชื่อถือและมีความปลอดภัยสูงสุด ไม่ต้องไปมองหาที่ไหนอีกแล้ว! ขอแนะนำ สล็อตเว็บตรง 100% ที่ ไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์
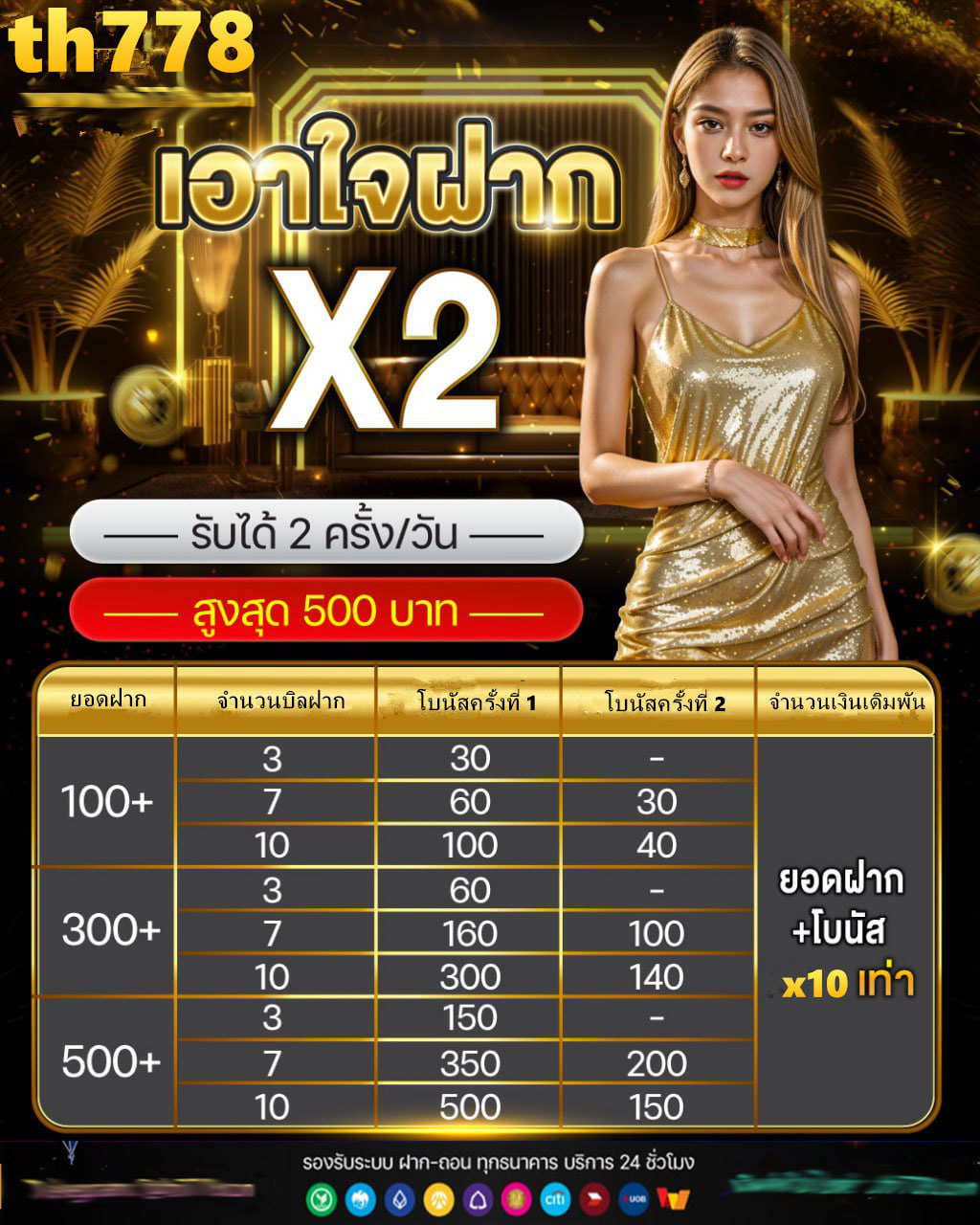
th38 สล็อต ทางเข้า buddy88 โปรโมชั่นมีมากมายหลากหลายรูปแบบ แจกเป็นทุนการเล่นฟรีให้กับสมาชิกเป็นจำนวนมากอยู่ตลอดเวลา และยังมีการแจกเป็นเงินสดให้แบบไม่อั้นอีกด้วย
เกม สล็อต zabbet168 Buddy88สล็อต เป็นหนึ่งในเว็บพนันออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมอย่างมากในขณะนี้ ด้วยการเป็นเว็บตรงที่ไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ทำให้ผู้เล่นมั่นใจได้ถึงความปลอดภัย และความยุติธรรมที่ได้รับจากการเล่นเกม
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pgสาวถ้ำ สล็อต · โปรโมชั่น · ติดต่อเรา · บทความ บทความ buddy88 คาสิโนออนไลน์ อันดับ 1 ในประเทศไทย สมัครฟรีลุ้น โบนัสแตกทุกวัน Copyright © 2025
Add to wish list- SKU:615941142
- Category:Game
- Tags:buddy88 สล็อต
Product description
buddy88 สล็อตbuddy88 สล็อต ✅ buddy88 - buddy88 เกมพนันออนไลน์ จ่ายหนัก ไม่อั้น จัดเต็มทุกวัน buddy88 สล็อต,buddy88 หากคุณกำลังมองหา เว็บสล็อต ที่น่าเชื่อถือและมีความปลอดภัยสูงสุด ไม่ต้องไปมองหาที่ไหนอีกแล้ว! ขอแนะนำ สล็อตเว็บตรง 100% ที่ ไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ &emspเว็บไซต์รวมเกมคุณภาพดี Buddy88 ฝาก10 รับ 100 ล่าสุด เข้าเล่นได้โดยตรง ตลอด 24 ชั่วโมง ครบทุกรูปแบบ Q&A คำถามที่พบบ่อย Q: ทุกเกมสล็อตจะสามารถทำกำไรได้อย่างไร; Q: ระบบทดลองเล่นใช้งาน